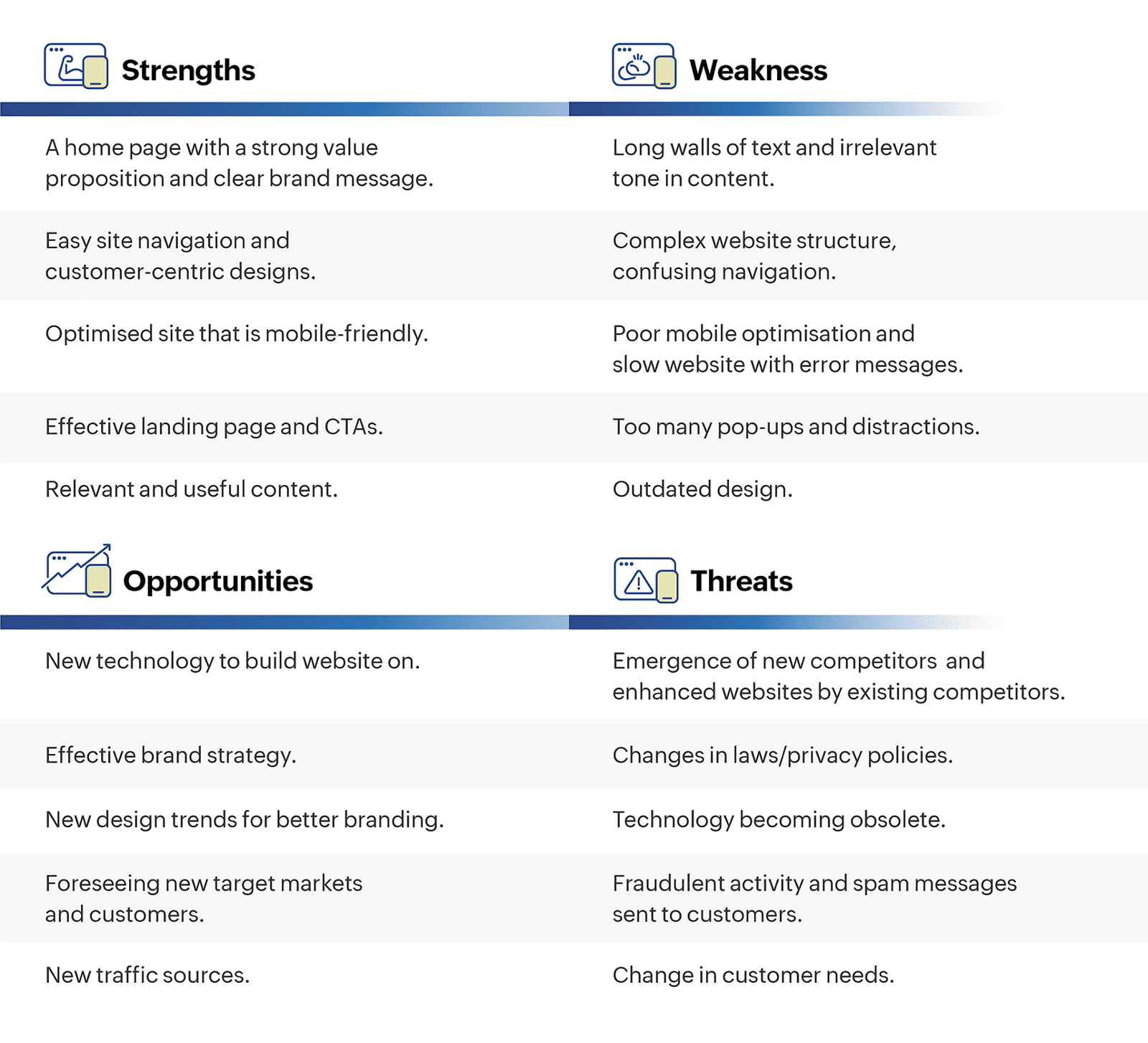
Why review your website?
Does your website still represent what your company offers?
Why review your website?
Who: Who are you? Who are you representing? Who do you provide services for?
What: What value do you offer? What products do you sell? What training certifications do you have?
When: When did you start your business? When do you post resources on your website? When were those resources last updated?
Where: Where are you located? Where is your target audience located? Where did you source the information on your website? Where do the links on your website redirect to?
Why: Why are you passionate about what you do? Why should someone choose your service?
Which: Which product is your specialty? Which countries or regions do you serve?
How: How can you be contacted? How are you better than your competitors?

- Typography & font
- Social media designs & images
Specific
Measurable
Attainable
Relevant
Time-bound
Link for design ideas
Just by navigating a competitor’s site on your own, you can assess factors like its search ranking, UI, content, localization, and social media integrations. You can even load it up on your phone to see if the site’s appearance is mobile-friendly.

A wireframe is like an architectural blueprint for your website. It should provide a clear outline of your website’s new structure, layout, information architecture, user flow, and functionality. You can design it with pen and paper or digital site mapping tools, and the amount of detail you add will classify it as low, mid, or high fidelity.
This may seem like a minor step, but it’s important not to skip it. A wireframe is meant to be shared with your stakeholders, introducing a critical review stage in your website design process. This is a great opportunity for low-stakes feedback, and it ensures everyone is on the same page about the website changes before they go into design and development. This will save you time and money, and involving your stakeholders will show that you value their input and suggestions.

Content may be king, but your website’s design is where most users will make their first impression about your organization. If the design is poor, they won’t bother engaging with the content.
When redesigning your website, identify key pages to work on, create a minimum viable page, and then build on it to create additional pages. Here are some places to help you get started:

SEO is a cost-effective way to help you stay in the league.
Here are some useful SEO tips for your content:
Sitemap – An updated sitemap will ensure your site is indexed but duplicate content on your site is not.
Site architecture – Ensure that you have what’s called a “flat structure,” where all your pages are just a few links away from each other.
URL – You can optimize your URL by structuring it logically and consistently. Try including target keywords you want to rank for.
Schema markups – A schema markup is a code that you can add to your website’s back end to give search engines more context about your site content. This allows the algorithm to know when to display your content for relevant search queries and what rich snippets to add to those displays.
Page speed – Slow load times equal high bounce rates. The point of the internet is to find answers fast! These days, that translates to load times that are less than 3 seconds. Try using a page analysis tool to measure your load times.
Meta tags – Include relevant keywords in your meta title and meta description.
Title tags – There should be a distinct difference between H1, H2, and H3 in your content.
Categories and tags – Use categories and tags to group your content. They makenavigation easier and enhance the accessibility of your content. Tags are specific labels that are usually 1-3 words long. Not only do these micro-categorise your content, but also makes it easier for search engines to index your content.
Keywords and phrases – Use a balanced mix of short and long-tail keywords throughout your content. A content management system can help you track the keywords you have used so far.
Alt tags – Use alt tags for all your images. These are added into an image’s HTML code to describe its appearance and function. Not only does this help boost your SEO, but it also gives your site better accessibility to people who rely on screen readers to surf the web.
Internal linking – Providing links to other relevant content on your site enhances user experience and encourages visitors to stay on your site for longer. It also helps search engines discover more pages on your site. That said, be sure to remove any broken links on your website.
EAT principle – EAT stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Including information about your team, their achievements, and your company goals are essential. Adding author profiles to your content helps you meet Google’s quality guidelines.
Your A/B testing process should follow these general steps:
Research the A/B testing tools available in your market, and see which tools suit your requirements and budget.
Observe your visitor’s behaviour and draw insights. Formulate a hypothesis on what would work better than your current version.
Identify variables and create variations you want to test based on your hypothesis.
Run your test once these variations are assigned to visitors. Make sure to use temporary redirects (302 redirects).
Measure their interactions and compare how each version performs.

Just having a great website is not enough on it’s own. Promotion is essential to staying ahead of the pack and gaining more visibility. Here are some ways to promote your website and content even if you are on a budget:
SEO/PPC – Rank on search engines by bidding for AdWords if you have the budget for it. For organic reach, use SEO with your web design and content to rank higher in search engine listings.
Social media marketing – Having an active presence on social media channels like LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Reddit can help spread the word about you. Posting content there and regularly interacting with users is a great way to build brand awareness.
Email marketing – This involves sending a mixture of product resources, service updates, and commercial emails to your email subscribers. Keep in mind to follow privacy guidelines while implementing this strategy.
PR – Public speaking engagements help you grow as an individual and evangelize your brand. Getting featured in articles and other media outlets is a great way to promote your brand.
Content marketing and promotional platforms – Build a reservoir of educational content like blogs, help resources, podcasts, and webinars to generate leads. This strategy creates value for customers while building more awareness through post traffic. In addition to posting on your own site, use platforms like Zest, Medium, Quora, Quuu promote, Growth hackers, and YouTube to further advertise your expertise.
Referral marketing – Word-of-mouth marketing and referrals are still some of the most foolproof promotion strategies. Especially in the SaaS market, where software is considered an investment, this works like magic.
Co-marketing – Collaborating with other brands and business partners to promote each other not only strengthens your business relationship but also helps you access new target audiences.

Who to turn to for help?
Who to turn to for help?
Customer Consulting Group work with online website building tools, online social management and integration with other products. We would love to get you started today!

